There are many aspects to bear in mind when choosing the electric vehicle that best suits your needs. Performance, capacity, manoeuvrability, battery characteristics… In this post we are going to focus on one of these aspects, an aspect that may be regarded as irrelevant but which is crucial for the logistics of a company’s vehicles: the type of power outlet they need in order to be charged.
Electric vehicles need to be connected to electrical currents to recharge their batteries and keep operating. Fuel has been replaced by electricity and petrol stations by sockets. A change that affords numerous advantages over vehicles with combustion engines. Not only because of the economic savings it entails, but also thanks to the convenience of being able to charge the vehicle at your own home, warehouse or establishment and the zero emissions sustainability.
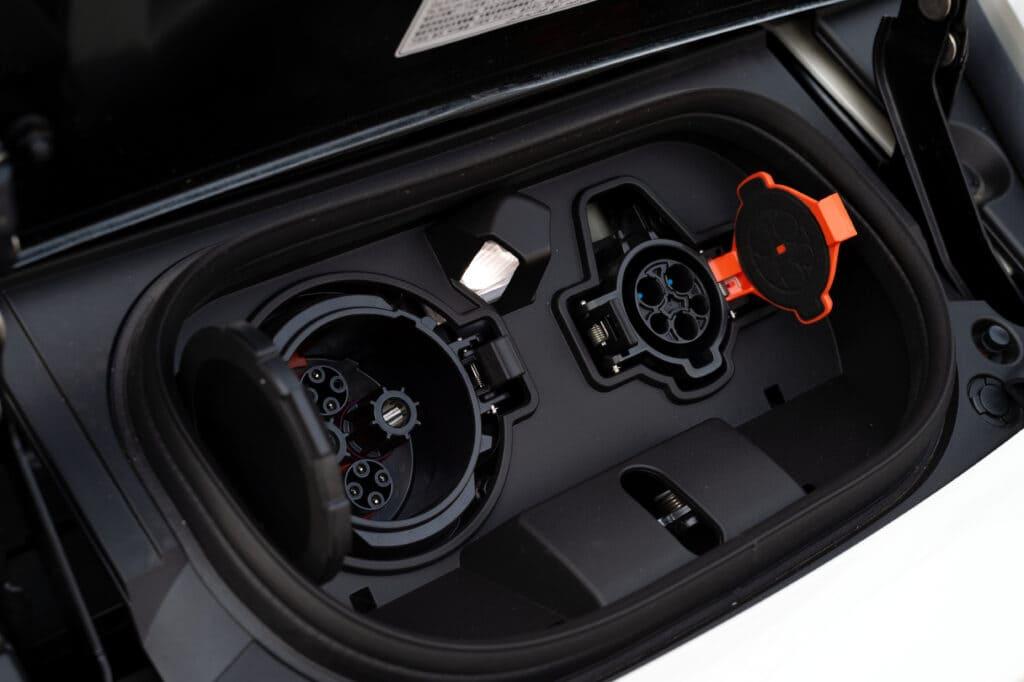
However, it is important to know the type of cable that fits each vehicle and to know how to distinguish between the power sockets where they can be charged: their differences, implications and accessibility according to the possibilities of each. Generally speaking, electric vehicles can be charged with direct current (DC) or with alternating current (AC) and practically all power sockets are only designed to work with one of these types of current, with some exceptions that allow them to work with both.
Power sockets for alternating current (AC) charging
Power outlets designed to work only with alternating current (AC) are the Schuko plug, the CEE plug, the Type 1 plug and the Type 2 plug. On the other hand, the CSS plug works with both alternating current and direct current.
- Schuko plug: has power of up to 3.7 kW and a voltage of 230V. Fits into normal household sockets and requires a Mode 2 cable. Bear in mind the cable that your vehicle will need to be charged correctly! And that there are cables with the same pin on both sides or with two different pins.
- Blue/red CEE plug: with power of up to 3.7 kW and up to 22 kW and voltage of 230V/400V. The blue CEE plug is also known as a “camping plug” and it requires a Mode 2 cable.
- Type 1 Plug: with power of up to 7.4 kW and voltage of 230V. It is common on Asian and North American vehicles and it requires a Mode 3 cable which can be used for much faster charging.
- Type 2 Plug: with domestic power of up to 22 kW and in public charging points of up to 43 kW and voltage of 400V. It is the standard plug in Europe and it requires a Mode 3 cable, compatible with fast charges.
- CSS plug: has power of up to 350 kW and voltage of 400V or more. This plug is a development of Type 2, it works with AC and DC and can only be recharged at a charging station.
Plugs for direct current (DC) charging
Plugs designed to work only with direct current (DC) are the CHAdeMo plug and also the CSS plug, which works with both alternating and direct current.
- CHAdeMo plug: has power of 200 kW or more and voltage of 300 V or more. It is used in Japanese vehicles and allows bidirectional charging, in addition, it can only be charged at a charging station.
Normal charging and fast charging
What do we mean by fast charging and by normal charging? Basically, fast charging is anything above 43 kW and normal charging is whatever is below that level. It’s important to know that a lot of electric vehicles are designed to allow fast charging, but not all of them: vehicles with small batteries don’t allow fast charging. You should also know that very fast charging is only possible with direct current and that most charging stations offer power of 50 kW (even 300 kW or more as regards those intended for ultra-fast charging). But make sure you don’t overuse these types of charging! They will test the batteries of your vehicles.
Inquieto’s Electric Vehicles
Inquieto’s electric bikes, three-wheelers, motorcycles, quadricycles and compact electric vans are charged using normal Schuko sockets. Which means they fit into normal household sockets and require a Mode 2 cable.